Research
The Living Lab 70 GW Offshore Wind – demand-oriented research for the energy transition
As part of the TEN.efzn network, the Living Lab is creating a unique research and innovation ecosystem in which a demand-oriented topic area with great scientific potential is addressing a holistic view of the expansion of wind energy in the German North Sea planned up to 2045 for the first time.
Demand-oriented research is characterized by
- Practical relevance: Our research questions on the expansion of offshore wind energy are derived directly from the real needs and challenges of the economy, society, politics and the environment.
- Application orientation: Our results will be usable in practice, e.g. in the form of tools, technologies, processes or recommendations for action.
- Interdisciplinarity: Within the framework of TEN.efzn and through the integration of different research disciplines, we address the complex challenges with a wide range of approaches.
- Stakeholder participation: The target groups of our research, e.g. companies, citizens, local authority associations, are involved in the design of research questions and the development of solutions.
- Problem orientation: The aim is to identify, analyze and solve specific challenges in the expansion of offshore wind energy, as defined in the individual innovation areas.
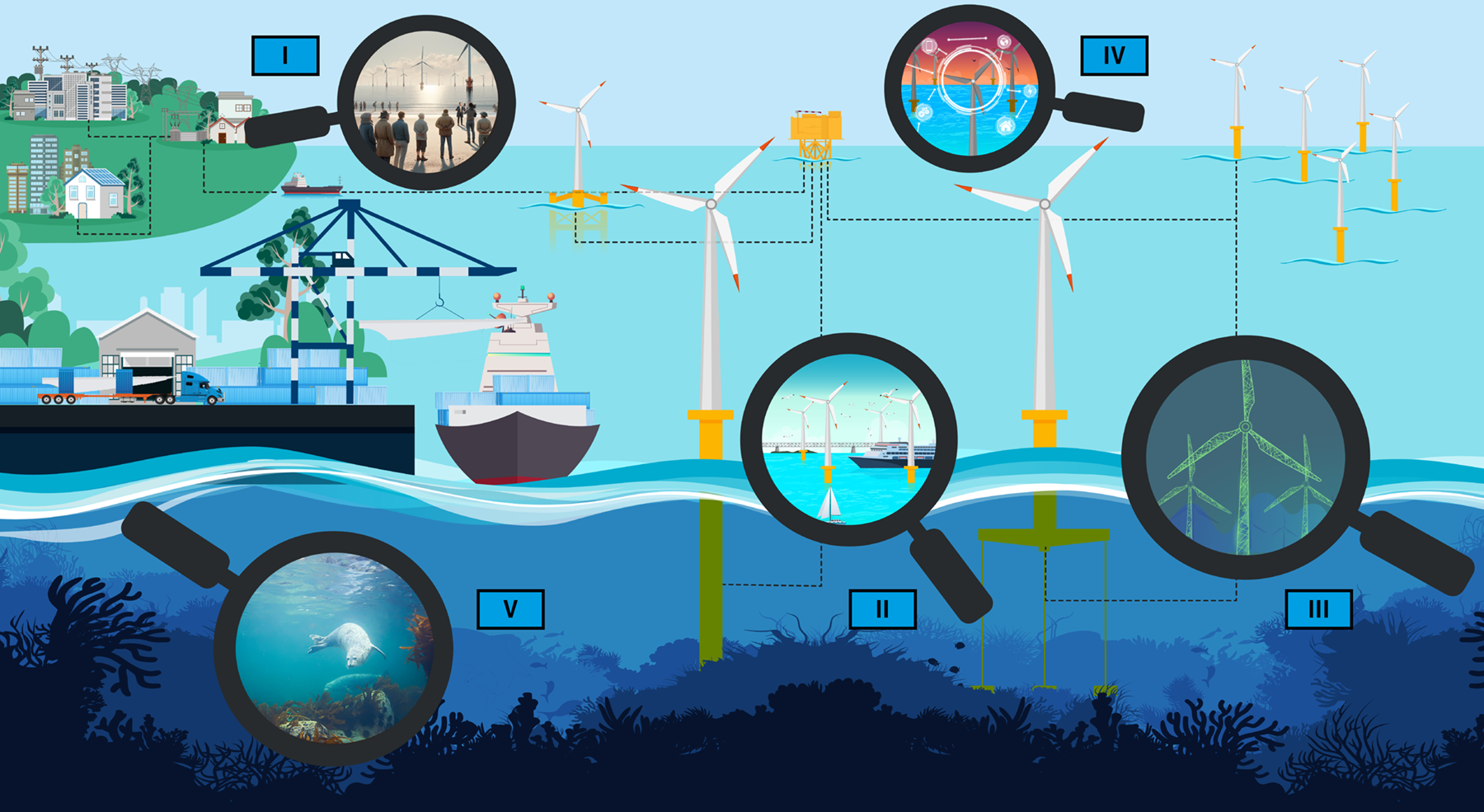
Approaches of the five innovation areas in the Living Lab
Innovation Area I analyzes social conflicts, opportunities and success factors of offshore expansion, develops participation processes and evaluates the expansion targets under various scenarios.
Innovation Area II uses models to plan sustainable expansion strategies and maritime spatial planning in the German Bight, taking into account economic aspects, tenders and co-utilization.
Innovation areas III and IV carry out measurement campaigns and simulations to analyze the aging of turbines, improve service lives and control new turbines more efficiently. This also serves to stabilize the grid feed-in.
Innovation Area V uses research vessels to investigate the effects of offshore wind energy on the marine environment and develops strategies to minimize negative effects and promote positive effects.
Innovation areas and sub-projects

Innovation Area I – Social and economic issues relating to the expansion of offshore wind energy
Motivation
The subject of Innovation Area I is the analysis of conflict potentials, opportunities and conditions for the success of offshore expansion, the design of the necessary participation processes and the evaluation of the expansion targets under various techno-economic scenarios. The knowledge gained should enable socially and economically viable, socially just and ecologically compatible marine and coastal management.
- Expert interviews and surveys of the various stakeholders
- Conception and organization of dialogue formats, regional transfer events
- Involvement and participation of the various stakeholders in the analysis and the development of implementation strategies
Initial situation
The expansion targets for offshore wind energy, which are being pursued under great time pressure, raise economic and social questions, without which the success of this elementary transformation project of the energy transition is in doubt.
Innovation area II – Sustainable maritime spatial planning and use of the German Bight
Motivation
Various co-utilization scenarios are being developed together with various stakeholders from research, industry, planning authorities, environmental protection associations/authorities and users of the maritime space. The results will be presented and compared in international forums in order to be able to transfer findings on large-scale expansion to the entire North Sea.
- Close integration with IB I in order to incorporate social and economic aspects into the assessment.
- Recommendations on how the expansion can be realized sustainably, especially beyond 50 GW.
Initial situation
Due to the limited area, the planned installed wind capacity in the German Bight is one of the densest offshore wind farms in the world. Models for sustainable spatial and land use planning are therefore to be further developed and validated with regard to co-use.
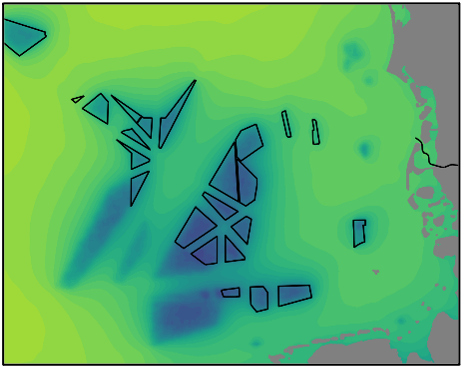

Innovation area III – Life cycle management of offshore wind turbines and wind farms
Motivation
In order to create scope for action through optimized operating scenarios and maintenance strategies when realizing offshore expansion targets, information on the state of health of individual wind turbines and offshore wind farms is essential. In innovation area III, the comprehensive analysis of structural and SCADA data using innovative methods of population-based structural health monitoring will create the necessary basis for central questions.
- Maintenance and repowering as the basis for a techno-economic assessment of the required expansion
- Extension of the remaining service life through optimized inspection and maintenance of support structures and rotor blades
Initial situation
The continuous availability of at least 70 GW of installed nominal capacity, even in phases of decommissioning and repowering of older wind farms, is crucially linked to issues of operation and a coordinated planning process.
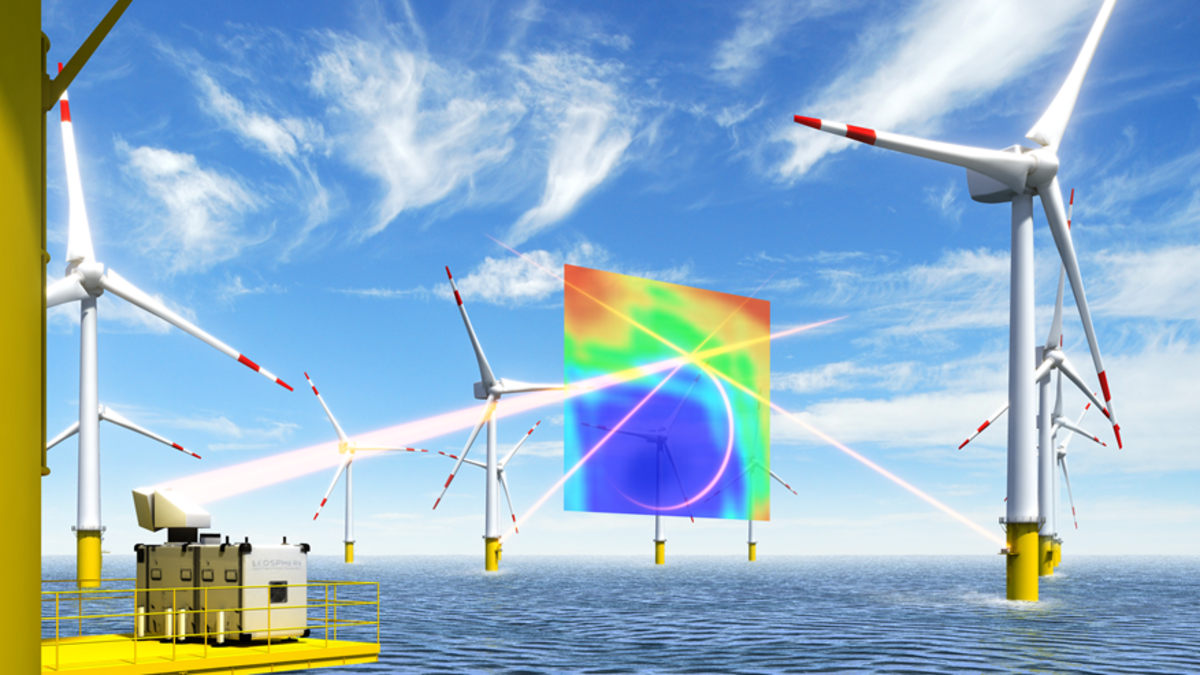
Innovation area IV – System-oriented integration and aerodynamics of offshore wind turbines and wind farms
Motivation
The focus is on two offshore measurement campaigns in wind farm clusters. This database will be used to reconstruct flow dynamics on different scales and enable predictions to be made. Higher wind turbines will reach into strong, laminar winds. The interaction of these flow conditions with turbines and their wakes will be examined in more detail using wind tunnel investigations.
- Quality-assured in-situ measurement campaign in two wind farm clusters. Networking with IB III, IV and V with simulations
- Operational optimization: power – grid integration – loads (operating time/costs)
Initial situation
In addition to the quantity, the quality of the wind energy fed into the grid is becoming increasingly important. At the same time, the rapid growth in the size of wind turbines and the densification of wind farm clusters are resulting in greatly changed inflow conditions that require new operating and control strategies.

Innovation area V – Marine load limits
Motivation
The overarching goal of Innovation Area V is to collect environmental-physical field data that can serve as a reliable basis for assessing the impact of offshore wind energy on the marine environment in order to develop comprehensive strategies in synergy with other research projects that record and reduce the undesirable effects of offshore wind energy on the marine environment.
- Assessment of the effectiveness of targeted mitigation concepts (“nature inclusive design”, analysis of “multi-use” potentials)
- Customized “what-if” scenarios for stakeholders and decision-makers
Initial situation
The considerable expansion of offshore wind energy capacity is being increasingly scrutinized by society due to its potential impact on the environment. However, the lack of a quality-assured data basis and the lack of understanding of site-specific factors make it difficult to assess environmental impacts.
Research partners
Our partners in the Living Lab Offshore
SFB Offshore Megastructures
For the operation of future wind farms, precise information about the condition and dynamic behavior of the support structure and rotor blades as well as knowledge about the effects of changing environmental and operating conditions is required for each individual turbine throughout its entire service life. Classic simulation models are usually identical for all turbines in a wind farm and focus primarily on the load-bearing capacity. Aspects such as production, installation, operation and dismantling, on the other hand, are given secondary consideration.
As part of the collaborative research center, the researchers are therefore developing a method that integrates all of these details: the digital twin. The digital twin is a coupled overall model of a specific wind turbine that is adapted to the current state of the real structure (the real twin) with the help of measurement data. This results in simulation models that describe individual, real turbines over their entire service life and can always be adapted to the current state.
Several research institutions have joined forces for the SFB 1463 “Integrated Design and Operation Methodology for Offshore Megastructures” under the leadership of Leibniz Universität Hannover (LUH): In addition to LUH, the Carl von Ossietzky University of Oldenburg, the German Aerospace Center, the Technical University of Dresden as well as the Technical University of Darmstadt and the University of the Federal Armed Forces Munich are involved. At Leibniz Universität, a total of ten institutes from the Faculties of Civil Engineering and Geodesy, Mechanical Engineering, Mathematics and Physics and Electrical Engineering and Computer Science are involved. The majority of the participating institutes at Leibniz Universität Hannover and Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg are already networked in the ForWind research association.
German Marine Research Alliance
Climate, seas and oceans are vital: they play a central role in global climate processes, are among the most important ecosystems on earth and are the basis of life for a growing world population. In order to preserve them as the basis of our lives in the future, we need knowledge for their protection and sustainable use by humans.
In 2019, German marine research, together with the federal government and the northern German states of Bremen, Hamburg, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Lower Saxony and Schleswig-Holstein, founded the German Marine Research Alliance (DAM) – one of the largest marine research alliances in the world. The aim of the DAM is to strengthen the sustainable management of the coasts, seas and oceans. With its activities in the core areas of research, data management and digitalization, coordination of infrastructures and transfer, the DAM works together with its member institutions and in exchange with politics, business and civil society to develop solution-oriented knowledge and options for action as a basis for sustainable decisions.